Cancer, also called malignancy, is an abnormal growth of cells.
There are more than 100 types of cancer including :
Anything that may cause a normal body cell to develop abnormally potentially can cause cancer; general categories of cancer-related or causative agents are as follows: chemical or toxic compound exposures, ionizing radiation, some pathogens, and human genetics.
Although there are many tests to screen and presumptively diagnose cancer, the definite diagnosis is made by examination of a biopsy sample of suspected cancer tissue.
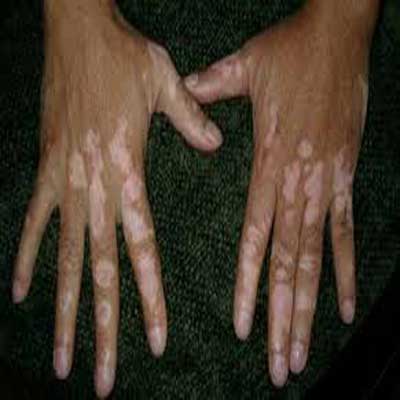
Vitiligo (vit-ih-LIE-go) is a disease that causes the loss of skin color in blotches. The extent and rate of color loss from vitiligo is unpredictable. It can affect the skin on any part of your body. It may also affect hair and the inside of the mouth.
Normally, the color of hair and skin is determined by melanin. Vitiligo occurs when the cells that produce melanin die or stop functioning. Vitiligo affects people of all skin types, but it may be more noticeable in people with darker skin. The condition is not life-threatening or contagious. It can be stressful or make you feel bad about yourself.
Symptoms:
The main sign of vitiligo is patchy loss of skin color. Usually, the discoloration first shows on sun-exposed areas, such as the hands, feet, arms, face and lips.
Vitiligo signs include:
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a joint disorder featuring inflammation. A joint is an area of the body where two different bones meet. A joint functions to move the body parts connected by its bones. Arthritis literally means inflammation of one or more joints.
Arthritis is frequently accompanied by joint pain. Joint pain is referred to as arthralgia. When four or more joints are involved, the arthritis is referred to as polyarthritis. When two or three joints are involved, it is referred to as oligoarthritis. When only a single joint is involved, it is referred to as monoarthritis.
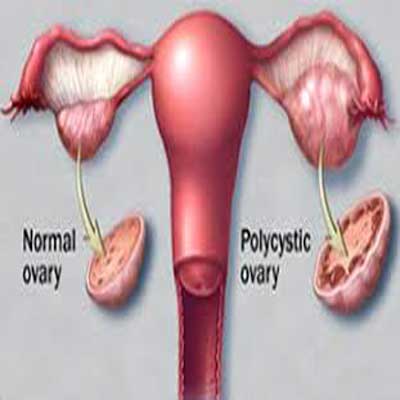
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods or excess male hormone (androgen) levels. The ovaries may develop numerous small collections of fluid (follicles) and fail to regularly release eggs.
Early diagnosis and treatment along with weight loss may reduce the risk of long-term complications such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Symptoms:
PCOS signs and symptoms are typically more severe if you're obese.
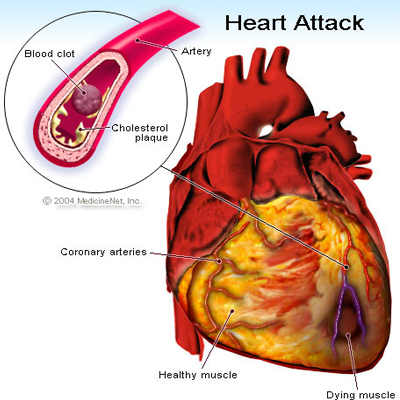
Unlike cardiovascular disease, which describes problems with the blood vessels and circulatory system as well as the heart, heart disease refers only issues and deformities in the heart itself.
Types:

Sterility is the physiological inability to effect sexual reproduction in a living thing, members of whose kind have been produced sexually. Sterility has a wide range of causes. It may be an inherited trait, as in the mule; or it may be acquired from the environment, for example through physical injury or disease, or by exposure to radiation.
Sterility can be caused by different closely related species breeding and producing offspring, these animals are usually sterile due to different numbers of chromosomes from the two parents, causing an imbalance in the resulting offspring making it viable but not fertile, this is the case with the mule. Sterility can also be caused by chromosomal differences within the patient, these individuals tend to be known as a genetic mosaics. Loss of part of a chromosome can also cause sterility due to nondisjunction. Sterility can also be caused by selective breeding, where the trait you are selecting for is closely linked to genes involved in sex determination or fertility, for example goats breed to be polled (hornless), this results in a high number of intersex individuals among the offspring, which are typically sterile. XX male syndrome is another cause of sterility, this is where the sexual determining factor on the Y chromosome (SRY) is transferred to the X chromosome due to an unequal crossing over, this gene indicated what gender the individual should be and causes the development of testes, causing the individual to be phenotypically male but genotypically female, the resulting individual is (information needed).

Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are passed from one person to another through sexual contact. The causes of STDs are bacteria, parasites, yeast, and viruses. There are more than 20 types of STDs, including
Most STDs affect both men and women, but in many cases the health problems they cause can be more severe for women. If a pregnant woman has an STD, it can cause serious health problems for the baby.
Antibiotics can treat STDs caused by bacteria, yeast, or parasites. There is no cure for STDs caused by a virus, but medicines can often help with the symptoms and keep the disease under control.
Correct usage of latex condoms greatly reduces, but does not completely eliminate, the risk of catching or spreading STDs. The most reliable way to avoid infection is to not have anal, vaginal, or oral sex.
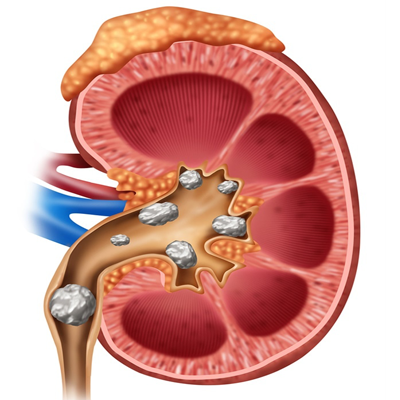
A kidney stone is a hard, crystalline mineral material formed within the kidney or urinary tract. Kidney stones can grow to the size of a golf ball while maintaining a sharp, crystalline structure. The stones may be small and pass unnoticed through the urinary tract, but they can also cause extreme pain as they leave the body.
Symptoms:
Kidney stones are small masses of salts and minerals that form inside the kidneys and may travel down the urinary tract. Kidney stones range in size from just a speck to as large as a ping pong ball. Signs and symptoms of kidney stones include blood in the urine, and pain in the abdomen, groin, or flank. About 5% of people develop a kidney stone in their lifetime.

Allergy involves an exaggerated response of the immune system, often to common substances such as foods or pollen.
The immune system is a complex system that normally defends the body against foreign invaders, such as bacteria and viruses, while also surveying for abnormal changes in an individual’s own cells, such as cancer.
An allergy refers to an exaggerated reaction by the immune system in response to exposure to certain foreign substances. The response is exaggerated because these foreign substances are normally seen by the body as harmless in nonallergic individuals and do not cause a response in them. In allergic individuals, the body recognizes the foreign substance, and the allergic part of the immune system generates a response.
Allergy-producing substances are called "allergens." Examples of allergens include pollens, dust mites, molds, animal proteins, foods, and medications. When an allergic individual comes in contact with an allergen, the immune system mounts a response through the IgE antibody. People who are prone to allergies are said to be allergic or "atopic."

Menstrual cycles often bring about a variety of uncomfortable symptoms leading up to your period. Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) encompasses the most common issues, such as mild cramping and fatigue, but the symptoms usually go away when your period begins.
However, other, more serious menstrual problems may also occur. Menstruation that is too heavy or too light, or the complete absence of a cycle, may suggest that there are other issues that are contributing to an abnormal menstrual cycle.
Remember that a “normal” menstrual cycle means something different for every woman. A cycle that’s regular for you may be abnormal for someone else. It’s important to stay in tune with your body and to talk to your doctor if you notice any significant changes to your menstrual cycle.
There are several different menstrual problems that you may experience.

Hemorrhoids (HEM-uh-roids), also called piles, are swollen veins in your anus and lower rectum, similar to varicose veins. Hemorrhoids have a number of causes, although often the cause is unknown. They may result from straining during bowel movements or from the increased pressure on these veins during pregnancy. Hemorrhoids may be located inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids), or they may develop under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids).
Hemorrhoids are very common. Nearly three out of four adults will have hemorrhoids from time to time. Sometimes they don't cause symptoms but at other times they cause itching, discomfort and bleeding.
Occasionally, a clot may form in a hemorrhoid (thrombosed hemorrhoid). These are not dangerous but can be extremely painful and sometimes need to be lanced and drained.
Fortunately, many effective options are available to treat hemorrhoids. Many people can get relief from symptoms with home treatments and lifestyle changes.
Signs and symptoms of hemorrhoids may include:
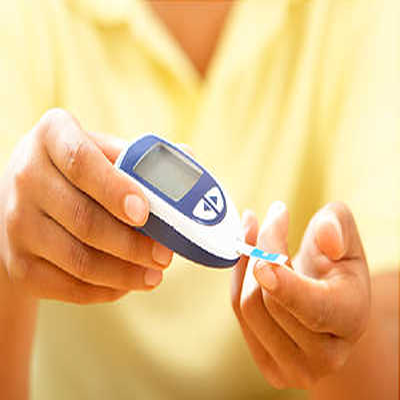

Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well. Without enough insulin, the glucose stays in your blood. You can also have prediabetes. This means that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Having prediabetes puts you at a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes - the body does not produce insulin. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1.
Type 2 Diabetes - the body does not produce enough insulin for proper function. Approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes worldwide are of this type.
Gestational Diabetes - this type affects females during pregnancy.
The most common diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, intense thirst and hunger, weight gain, unusual weight loss, fatigue, cuts and bruises that do not heal, male sexual dysfunction, numbness and tingling in hands and feet.
If you have Type 1 and follow a healthy eating plan, do adequate exercise, and take insulin, you can lead a normal life.
Type 2 patients need to eat healthily, be physically active, and test their blood glucose. They may also need to take oral medication, and/or insulin to control blood glucose levels.
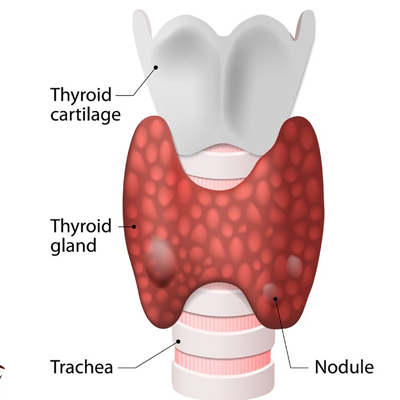
Thyroid disorders are conditions that affect the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck. The thyroid has important roles to regulate numerous metabolic processes throughout the body. Different types of thyroid disorders affect either its structure or function.
The thyroid gland is located below the Adam's apple wrapped around the trachea (windpipe). A thin area of tissue in the gland's middle, known as the isthmus, joins the two thyroid lobes on each side. The thyroid uses iodine to produce vital hormones. Thyroxine, also known as T4, is the primary hormone produced by the gland. After delivery via the bloodstream to the body's tissues, a small portion of the T4 released from the gland is converted to triiodothyronine (T3), which is the most active hormone.
The function of the thyroid gland is regulated by a feedback mechanism involving the brain. When thyroid hormone levels are low, the hypothalamus in the brain produces a hormone known as thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) that causes the pituitary gland (located at the base of the brain) to release thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to release more T4.
Since the thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, disorders of these tissues can also affect thyroid function and cause thyroid problems.
There are a variety of thyroid disorders, that can cause a variety of symptoms such as dry skin, constipation, depression, nervousness, fatigue, intolerance to heat or cold, weight loss, weight gain, increased sweating, and heart palpitations.
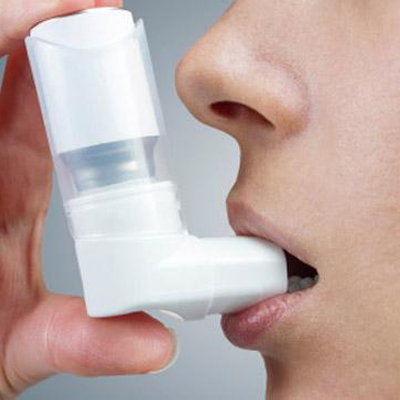

Asthma is a chronic disease involving the airways in the lungs. These airways, or bronchial tubes, allow air to come in and out of the lungs. If you have asthma your airways are always inflamed. They become even more swollen and the muscles around the airways can tighten when something triggers your symptoms.
Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath.
For some people, asthma is a minor nuisance. For others, it can be a major problem that interferes with daily activities and may lead to a life-threatening asthma attack.
Asthma can't be cured, but its symptoms can be controlled. Because asthma often changes over time, it's important that you work with your doctor to track your signs and symptoms and adjust treatment as needed.
Asthma signs and symptoms include:
Skin disorders vary greatly in symptoms and severity. They can be temporary or permament, and may be painless or painful. Some have situational causes, while others may be genetic. Some skin conditions are minor, and others can be life-threatening.
Common skin conditions include:
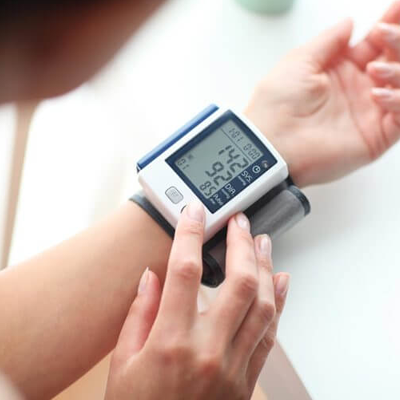

When your heart beats, it pumps blood round your body to give it the energy and oxygen it needs. As the blood moves, it pushes against the sides of the blood vessels. The strength of this pushing is your blood pressure. If your blood pressure is too high, it puts extra strain on your arteries (and your heart) and this may lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Having high blood pressure (hypertension) is not usually something that you feel or notice. It does not tend to produce obvious signs or symptoms. The only way to know what your blood pressure is, is to have it measured.
Your blood pressure naturally goes up and down all the time, adjusting to your heart’s needs depending on what you are doing. High blood pressure is when your blood pressure is persistently higher than normal.
A blood pressure reading under 120/80mmHg is considered optimal. Readings over 120/80mmHg and up to 139/89mmHg are in the normal to high normal range.
Blood pressure that’s high over a long time is one of the main risk factors for heart disease. As you get older, the chances of having persistently high blood pressure increases.
It’s very important to get your blood pressure checked regularly, and if it’s persistently high it needs to be controlled. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to a heart attack or stroke. It may also affect your kidneys.

A mental illness is a disease that causes mild to severe disturbances in thought and/or behavior, resulting in an inability to cope with life’s ordinary demands and routines.
There are more than 200 classified forms of mental illness. Some of the more common disorders are depression, bipolar disorder, dementia, schizophrenia and anxiety disorders. Symptoms may include changes in mood, personality, personal habits and/or social withdrawal.
Mental health problems may be related to excessive stress due to a particular situation or series of events. As with cancer, diabetes and heart disease, mental illnesses are often physical as well as emotional and psychological. Mental illnesses may be caused by a reaction to environmental stresses, genetic factors, biochemical imbalances, or a combination of these. With proper care and treatment many individuals learn to cope or recover from a mental illness or emotional disorder.
Symptoms:

Constipation is a condition of the digestive system where an individual has hard feces that are difficult to expel. In most cases, this occurs because the colon has absorbed too much water from the food that is in the colon.